News and Announcements
New staff member: Peter Scheepers
November 13, 2024
We welcome to Peter Scheepers who joined our group in November 2024.New IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology article
November 07, 2024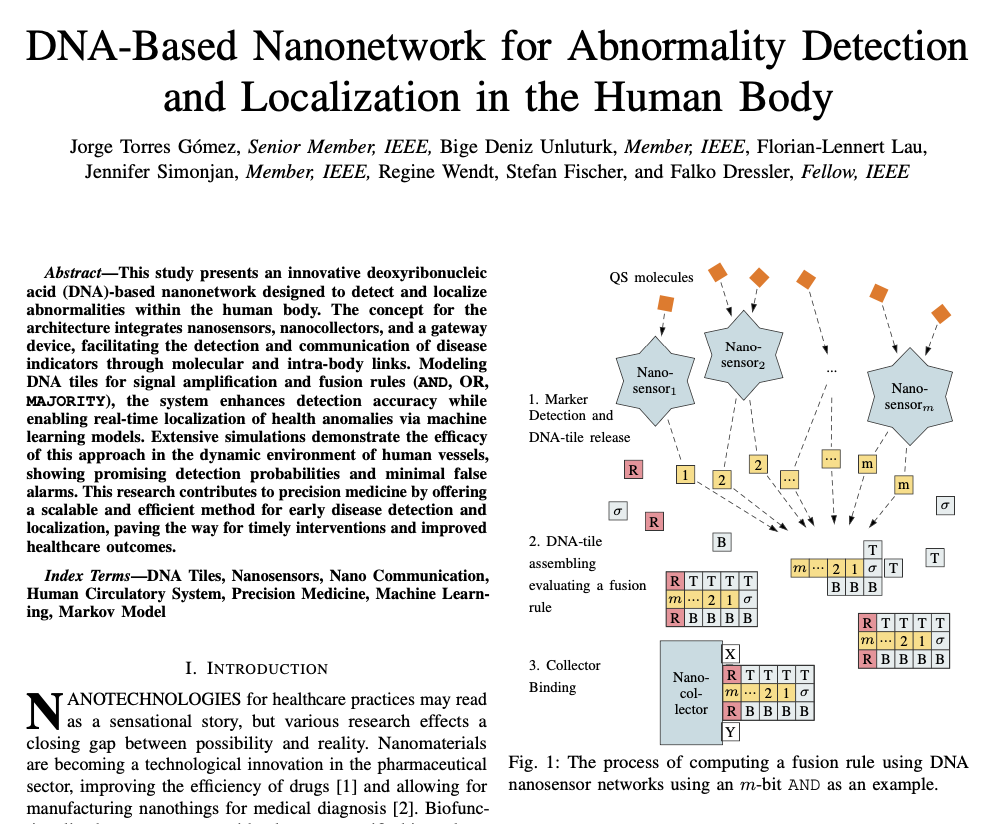
Our article DNA-Based Nanonetwork for Abnormality Detection and Localization in the Human Body has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology. This study presents an innovative deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-based nanonetwork designed to detect and localize abnormalities within the human body. The concept for the architecture integrates nanosensors, nanocollectors, and a gateway device, facilitating the detection and communication of disease indicators through molecular and intra-body links. Modeling DNA tiles for signal amplification and fusion rules (AND, OR, MAJORITY), the system enhances detection accuracy while enabling real-time localization of health anomalies via machine learning models. Extensive simulations demonstrate the efficacy of this approach in the dynamic environment of human vessels, showing promising detection probabilities and minimal false alarms. This research contributes to precision medicine by offering a scalable and efficient method for early disease detection and localization, paving the way for timely interventions and improved healthcare outcomes.
(link to more information)New IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing article
November 01, 2024
Our article Biasing Federated Learning with A New Adversarial Graph Attention Network has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing. Fairness in Federated Learning (FL) is imperative not only for the ethical utilization of technology but also for ensuring that models provide accurate, equitable, and beneficial outcomes across varied user demographics and equipment. This paper proposes a new adversarial architecture, referred to as Adversarial Graph Attention Network (AGAT), which deliberately instigates fairness attacks with an aim to bias the learning process across the FL. The proposed AGAT is developed to synthesize malicious, biasing model updates, where the minimum of Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the user's model update and the global model is maximized. Due to a limited set of labeled input-output biasing data samples, a surrogate model is created, which presents the behavior of a complex malicious model update. Moreover, a graph autoencoder (GAE) is designed within the AGAT architecture, which is trained together with sub-gradient descent to reconstruct manipulatively the correlations of the model updates, and maximize the reconstruction loss while keeping the malicious, biasing model updates undetectable. The proposed AGAT attack is implemented in PyTorch, showing experimentally that AGAT successfully increases the minimum value of KL divergence of benign model updates by 60.9% and bypasses the detection of existing defense models. The source code of the AGAT attack is released on GitHub.
(link to more information)Paper Presentation at ACM Nanocom 2024
October 29, 2024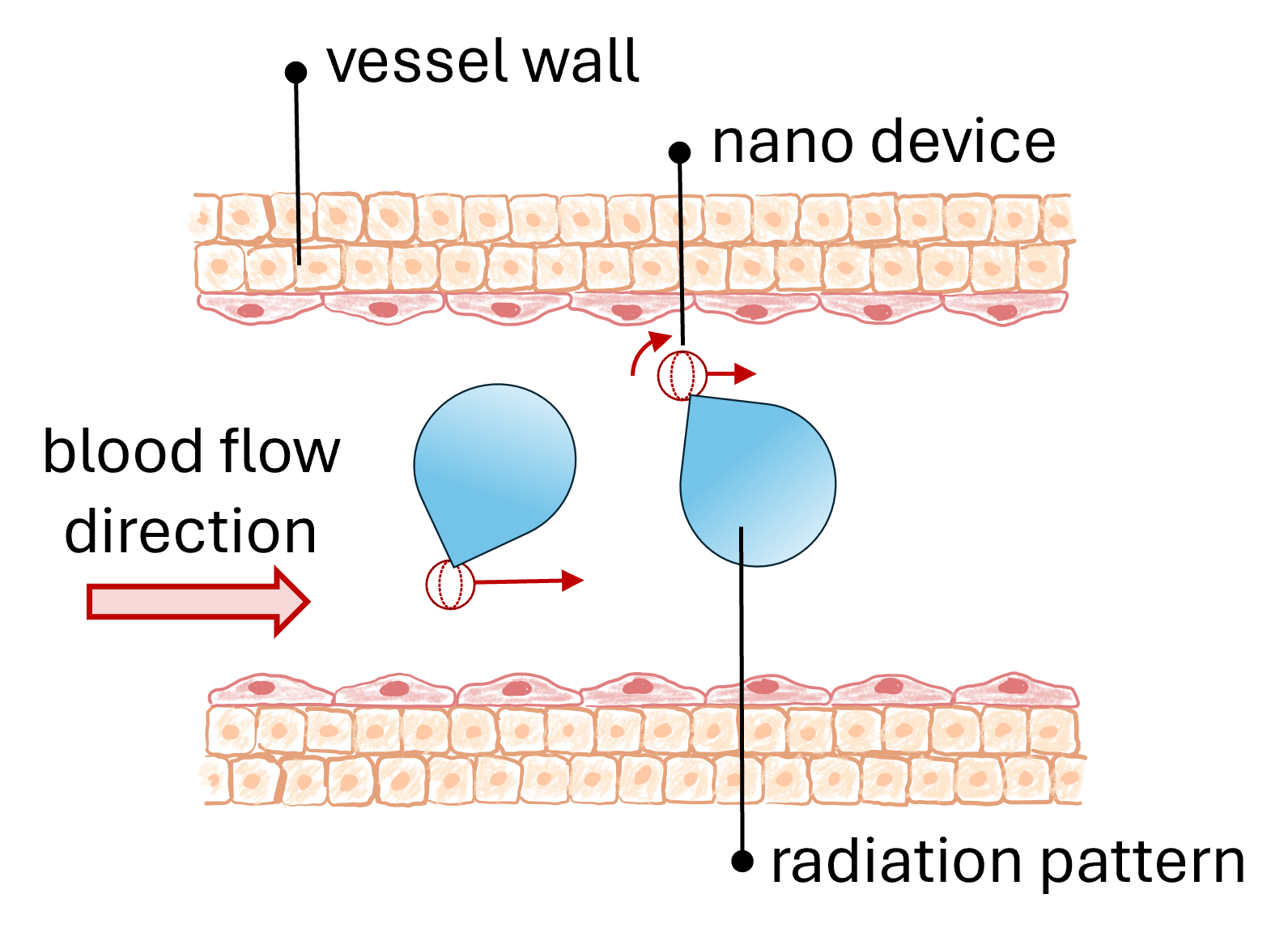
Mobility matters in the nanoscale to implement the connection among nanosensors. Analyzing the terahertz band, Jorge Torres Gómez presented our paper titled Implications of Nanodevice Mobility on Terahertz Communication Links in the Human Vessels at the 11th ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication (NanoCom 2024). We provide a model to evaluate the impact of mobility in the higher layers and implements a realistic model for the displacement, rotation, and power radiation of nanoantennas in the human vessels. The paper aims to guide the design of future protocols in nanonetworks.Paper Presentation at ACM NanoCom 2024
October 29, 2024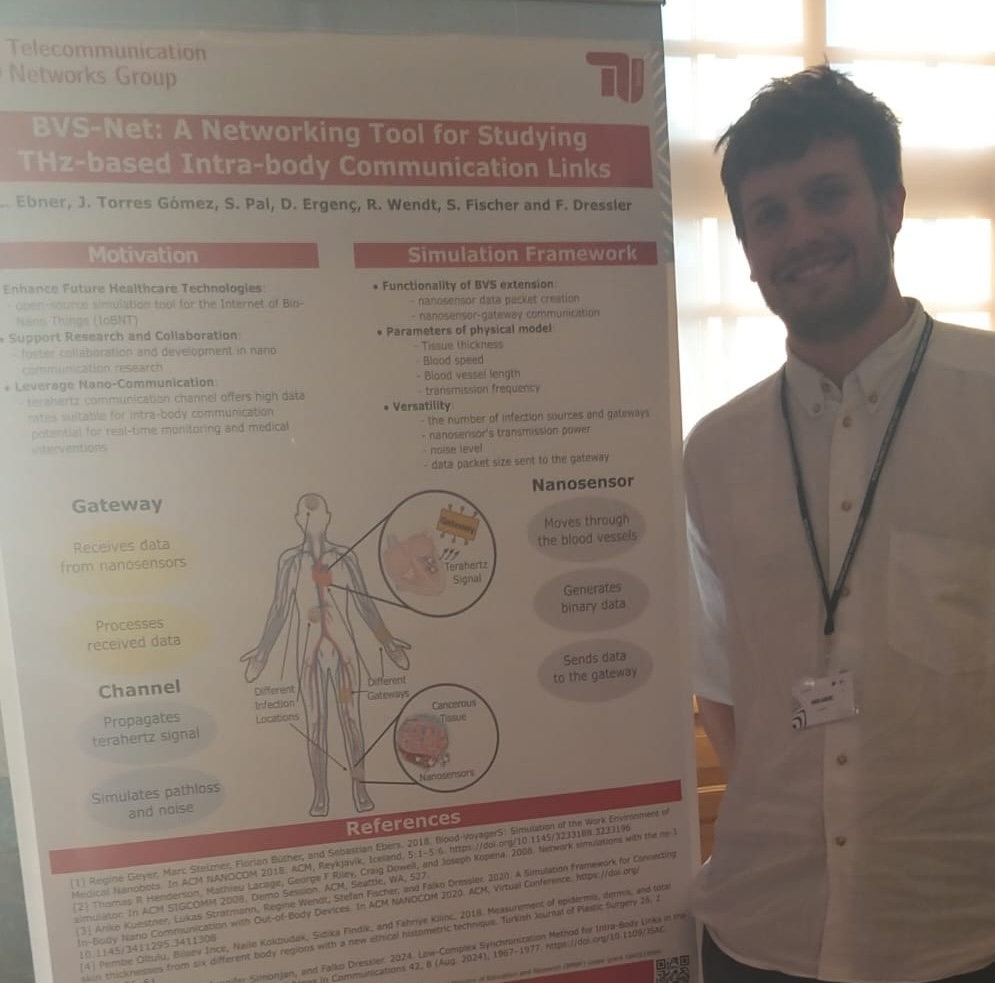
Delving into simulators for the Internet of Bio-Nano-Things (IoBNT) frameworks, our student member Laurenz Elbner presented the paper BVS-Net: A Networking Tool for Studying THz-based Intra-body Communication Links at the 11th ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication (NanoCom 2024). This research focuses on the communication of in-body nanobots with an out-of-body gateway to evaluate data transmission efficiency, identify potential obstacles, and optimize their design for practical applications. In particular, we introduce BVS-Net, an ns-3 module that models the terahertz communication channel between the nanobots and the external gateway.Invited talk at IEEE NPSM 2024
October 28, 2024
Our group member Dr. Doganalp Ergenc gave an invited talk titled Towards Time-sensitive Wireless Networks: Challenges, Opportunities, and Research Directions at the Networking Protocols and Standards for Mobility (NPSM 2024) workshop, which is organized under the 32nd IEEE International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP 2024) in Charleroi, Belgium.
(link to more information)Paper Presentation at IEEE 6GNet 2024
October 24, 2024
Our group member Osman Tugay Basaran presented our paper XAInomaly: Explainable, Interpretable, and Trustworthy AI for xURLLC in 6G Open-RAN at the 3rd International Conference on 6G Networking (6GNet 2024) at the Orange Gardens in Paris, France. Our paper introduces the "XAInomaly Framework", which incorporates our novel technique called fastSHAP-C. This method significantly enhances the explainability of AI models in 6G networks Next-generation URLLC (xURLLC) use case, providing a 25% improvement in resource utilization over existing approaches.Second Resilient Worlds research school
October 23, 2024
We organized the second research school on "Bulding Resilient Worlds - in Career and Research" in the context of the DFG priority program, Resilient Worlds! For two days, 16 early career researchers from several universities gave research talks, and attended workshops and hackathons to build resilience in both for their academic career and research. Besides organizing the event, our group member Dr. Doganalp Ergenc also gave a tutorial on the network simulator OMNeT++ and instructed a hackathon for using this tool to experiment on new Wi-Fi standard for network resilience.
(link to more information)Paper Presentation at IEEE LCN 2024
October 10, 2024
Our group member Sascha Rösler presented our paper Passive Device-Free Indoor Movement Detection Using WiFi Time-Of-Flight Information yesterday at the 49th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN 2024), Caen, Normandy, France. In our paper we show that the easily accessible time of flight data of WiFi FTM can be used to detect movements within a room. Our approach is around 10 percentage points better than a state of the art RSSI approach. We propose an architecture where already installed WiFi APs can be used together with a central server running a one-class SVMNew Elsevier Computer Networks article
October 08, 2024
Our article AI/ML-based Services and Applications for 6G-Connected and Autonomous Vehicles has been accepted for publication in Elsevier Computer Networks. AI and ML emerge as pivotal in overcoming the limitations of traditional network optimization techniques and conventional control loop designs, particularly in addressing the challenges of high mobility and dynamic vehicular communications inherent in the domain of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs). The survey explores the contributions of novel AI/ML techniques in the field of CAVs, also in the context of innovative deployment of multilevel cloud systems and edge computing as strategic solutions to meet the requirements of high traffic density and mobility in CAV networks. These technologies are instrumental in curbing latency and alleviating network congestion by facilitating proximal computing resources to CAVs, thereby enhancing operational efficiency also when AI-based applications require computationally-heavy tasks. A significant focus of this survey is the anticipated impact of 6G technology, which promises to revolutionize the mobility industry. 6G is envisaged to foster intelligent, cooperative, and sustainable mobility environments, heralding a new era in vehicular communication and network management. This survey comprehensively reviews the latest advancements and potential applications of AI/ML for CAVs, including sensory perception enhancement, real-time traffic management, and personalised navigation.
(link to more information)
Load all older news
Last modified: 2024-04-28