News and Announcements
Distributed Age-of-Information Scheduling with NOMA via Deep Reinforcement Learning
October 24, 2024
Many emerging applications in edge computing require processing of huge volumes of data generated by end devices, using the freshest available information. In this paper, we address the distributed optimization of multi-user long-term average Age-of-Information (AoI) objectives in edge networks that use NOMA transmission. This poses a challenge of non-convex online optimization, which in existing work often requires either decision making in a combinatorial space or a global view of entire network states. To overcome this challenge, we propose a reinforcement learning-based framework that adopts a novel hierarchical decomposition of decision making. Specifically, we propose three different types of distributed agents to learn with respect to efficiency of AoI scheduling, fairness of AoI scheduling, as well as a high-level policy balancing these potentially conflicting design objectives. Not only does the proposed decomposition improve learning performance due to disentanglement of different design objectives/rewards, but it also enables the algorithm to learn the best policy while also learning the explanations - as actions can be directly compared in terms of the design objectives. Our evaluations show that the proposed algorithm improves the long-term average AoI by 200% - 300% and 400% Congwei Zhang, Yifei Zou, Zuyuan Zhang, Jorge Torres Gómez, Tian Lan, Falko Dressler and Xiuzhen Cheng, "Distributed Age-of-Information Scheduling with NOMA via Deep Reinforcement Learning," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, September 2024. (online first)
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Congwei Zhang, Yifei Zou, Zuyuan Zhang, Jorge Torres Gómez, Tian Lan, Falko Dressler and Xiuzhen Cheng, "Distributed Age-of-Information Scheduling with NOMA via Deep Reinforcement Learning," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, September 2024. (online first)
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Age of Information-based Abnormality Detection with Decay in the Human Circulatory System
September 15, 2024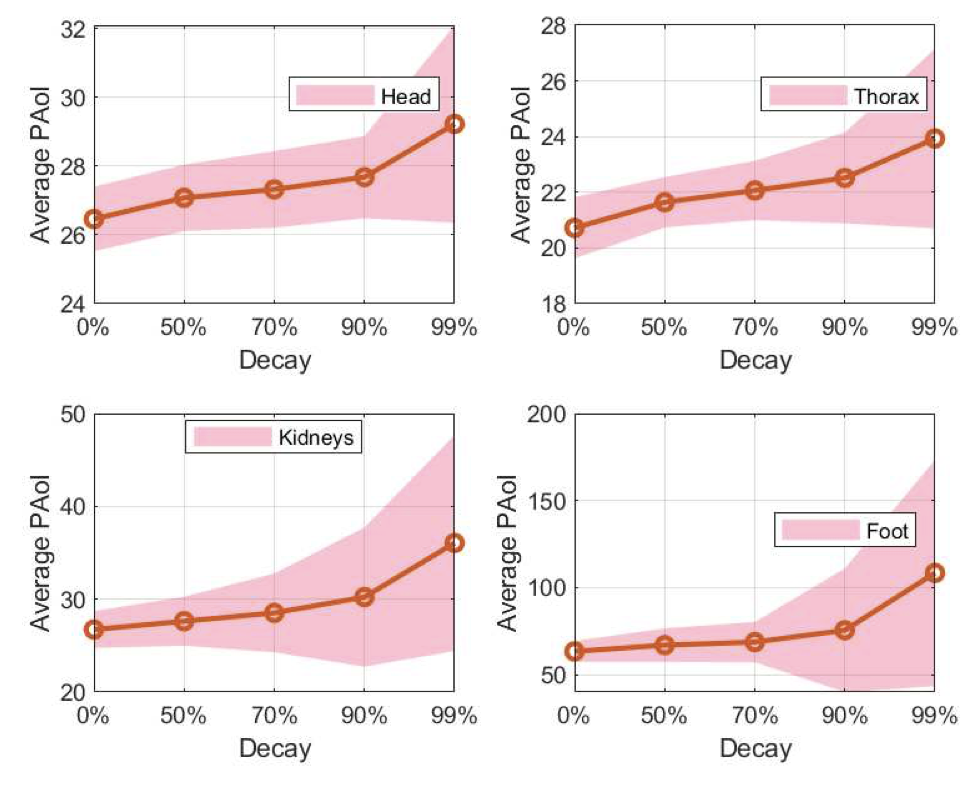
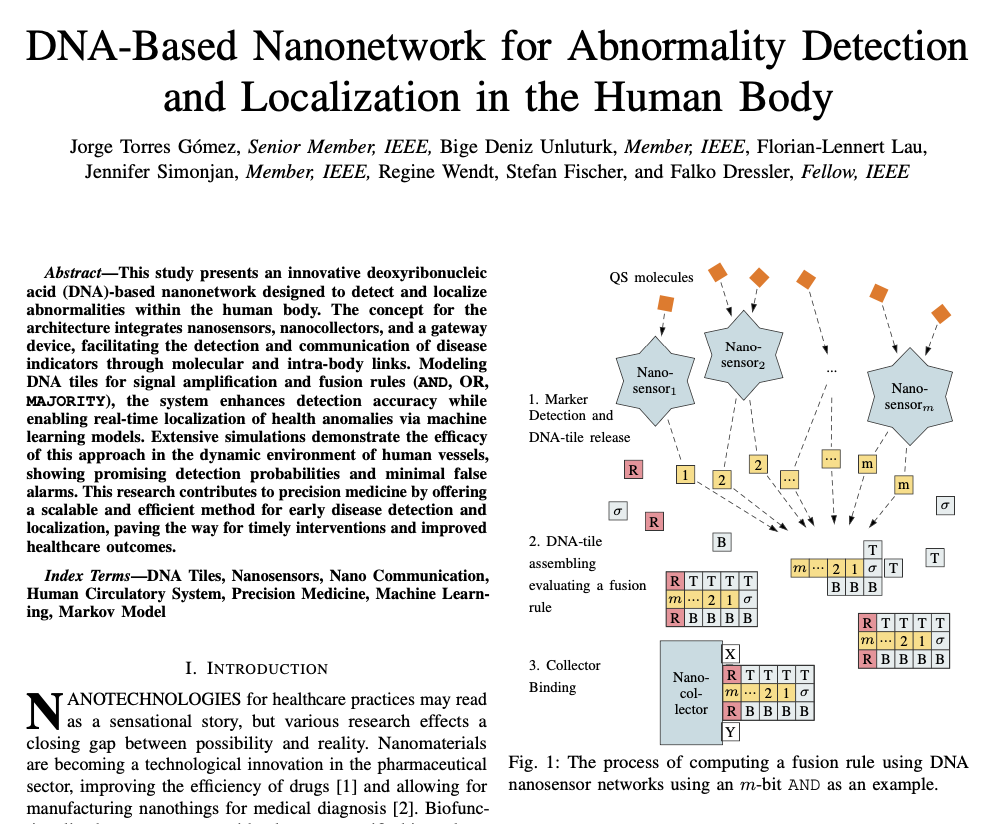
Detecting abnormalities early by deploying a network of mobile nanosensors within the human body remains a challenging task. Current methods for abnormality detection rely on placing gateways at arbitrary locations. In this work, we conducted an analysis of the impact of gateway placement and infection locations on detection time, detection ratio, and the average Peak Age of Information (PAoI). Our results revealed that the favorable gateway position is at the heart, minimizing detection time and enhancing the detection ratio for various infection locations. Furthermore, we observed that the detection ratio exhibited reduced variance with increased decay rates in nanosensors. Analyzing the PAoI across varying decay rates highlighted the importance of nanosensor quantity in relation to decay rate in ensuring accurate and timely infection localization. Saswati Pal, Jorge Torres Gómez, Regine Wendt, Stefan Fischer and Falko Dressler, "Age of Information-based Abnormality Detection with Decay in the Human Circulatory System," IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 10 (3), pp. 487–492, September 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Saswati Pal, Jorge Torres Gómez, Regine Wendt, Stefan Fischer and Falko Dressler, "Age of Information-based Abnormality Detection with Decay in the Human Circulatory System," IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 10 (3), pp. 487–492, September 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Using Ranging for Collision-Immune IEEE 802.11 Rate Selection with Statistical Learning
August 10, 2024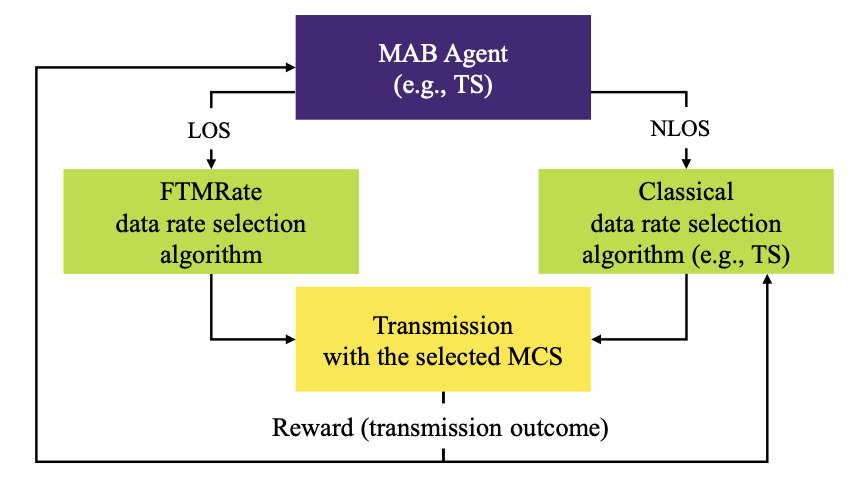
Appropriate data rate selection at the physical layer is crucial for Wi-Fi network performance: too high rates lead to loss of data frames, while too low rates cause increased latency and inefficient channel use. Most existing methods adopt a probing approach and empirically assess the transmission success probability for each available rate. We avoid this issue by resorting to the fine timing measurement (FTM) procedure, part of IEEE 802.11, which allows stations to perform ranging, i.e., measure their spatial distance to the AP. Since distance is not affected by sporadic distortions such as internal and external channel interference, we use this knowledge for data rate selection. Specifically, we propose FTMRate, which applies statistical learning (a form of machine learning) to estimate the distance based on measurements, predicts channel quality from the distance, and selects data rates based on channel quality. Wojciech Ciezobka, Maksymilian Wojnar, Krzysztof Rusek, Katarzyna Kosek-Szott, Szymon Szott, Anatolij Zubow and Falko Dressler, "Using Ranging for Collision-Immune IEEE 802.11 Rate Selection with Statistical Learning," Elsevier Computer Communications, vol. 225, pp. 10–26, September 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Wojciech Ciezobka, Maksymilian Wojnar, Krzysztof Rusek, Katarzyna Kosek-Szott, Szymon Szott, Anatolij Zubow and Falko Dressler, "Using Ranging for Collision-Immune IEEE 802.11 Rate Selection with Statistical Learning," Elsevier Computer Communications, vol. 225, pp. 10–26, September 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Where to Decide? Centralized vs. Distributed Vehicle Assignment for Platoon Formation
July 17, 2024
Optimized platoon formation is crucial for achieving best performance in terms of travel time and energy consumption. We explore the computation of vehicle-to-platoon assignments based on similarity between vehicles focusing on desired driving speed and current position on the road. We developed three approaches to solve this assignment problem: a centralized solver and a centralized as well as a distributed greedy heuristic. We performed a large-scale simulation study using PlaFoSim to compare all approaches. The centralized solver approach assumes global knowledge and requires a complex MIP solver to compute vehicle-to-platoon assignments. The centralized greedy approach, however, suffers from synchronization and greedy selection effects. Overall, the distributed greedy approach achieves close to optimal results but requires least assumptions and complexity. Julian Heinovski and Falko Dressler, "Where to Decide? Centralized vs. Distributed Vehicle Assignment for Platoon Formation," IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 25 (11), pp. 17317–17334, November 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Julian Heinovski and Falko Dressler, "Where to Decide? Centralized vs. Distributed Vehicle Assignment for Platoon Formation," IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 25 (11), pp. 17317–17334, November 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Private Over-the-Air Federated Learning at Band-Limited Edge
June 20, 2024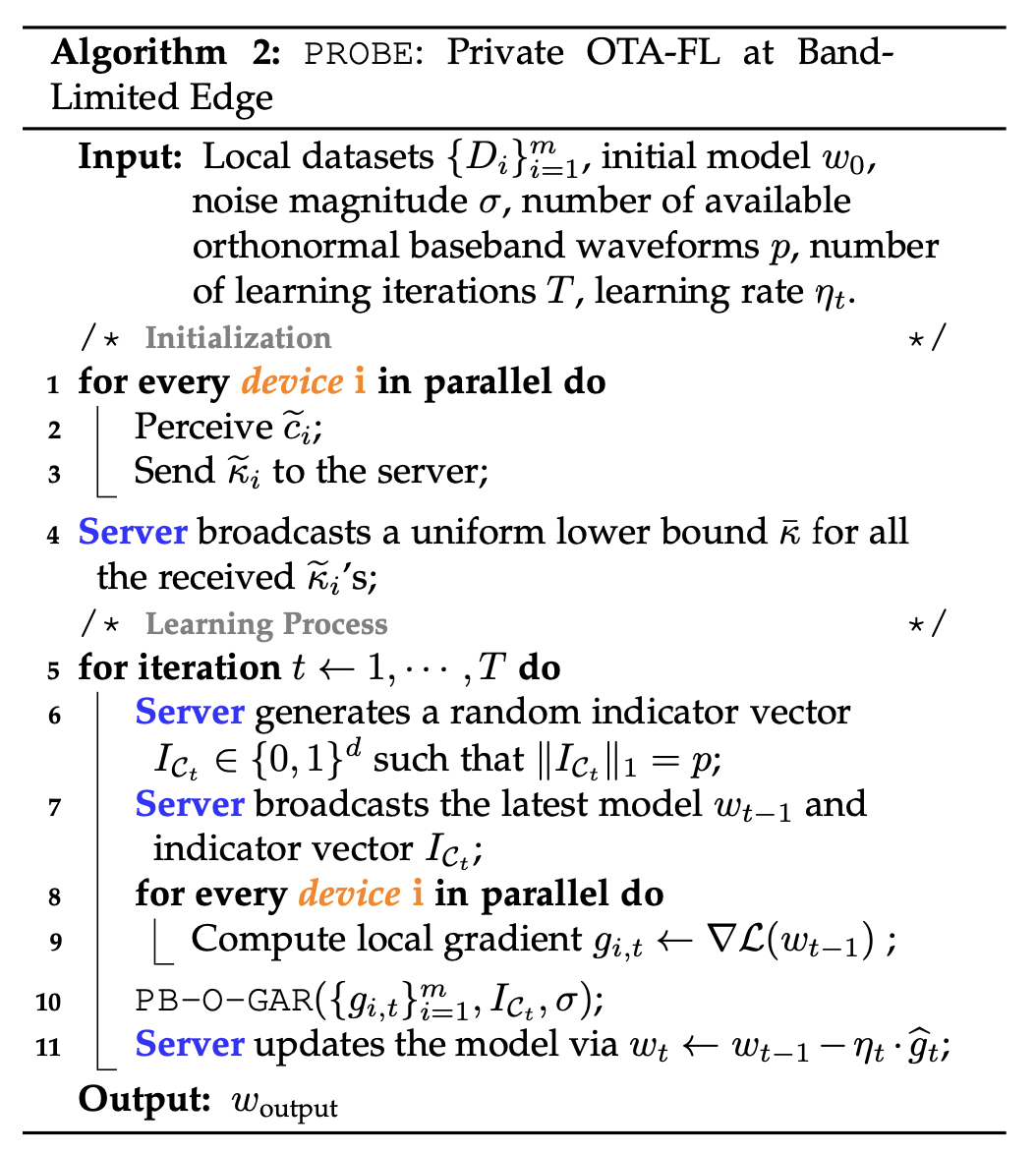
We investigate over-the-air federated learning (OTA-FL) that exploits over-the-air computing (AirComp) to integrate communication and computation seamlessly for FL. Privacy presents a serious obstacle for OTA-FL, as it can be compromised by maliciously manipulating channel state information (CSI). Moreover, the limited band at edge hinders OTA-FL from training large-scale models. It remains open how to enable a multitude of devices with constrained resources and sensitive data to collaboratively train a global model at band-limited edge. To tackle this, we design a novel algorithm PROBE building upon a lightweight over-the-air gradients aggregation rule PB-O-GAR. Specifically, PB-O-GAR combines a random sparsification-like dimension reduction with Gaussian perturbation to provide rigorous privacy and band-adapted communication. It elaborately calibrates the transmission signal according to devices' perceived CSI for heterogeneous power constraints accommodation and CSI attack resilience. We show that by utilizing the common randomness, which deviates from the conventional FL, random sparsification-like dimension reduction can augment privacy in addition to the intrinsic privacy amplification effect of AirComp. We establish near-optimal convergence rates and explicit trade-offs among privacy, communication and utility for PROBE. Finally, extensive experiments on benchmark datasets are conducted to validate our theoretical findings and showcase the superiority of PROBE in realistic settings. Youming Tao, Shuzhen Chen, Congwei Zhang, Di Wang, Dongxiao Yu, Xiuzhen Cheng and Falko Dressler, "Private Over-the-Air Federated Learning at Band-Limited Edge," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23 (12), pp. 12444–12460, December 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Youming Tao, Shuzhen Chen, Congwei Zhang, Di Wang, Dongxiao Yu, Xiuzhen Cheng and Falko Dressler, "Private Over-the-Air Federated Learning at Band-Limited Edge," IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23 (12), pp. 12444–12460, December 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Leverage Variational Graph Representation For Model Poisoning on Federated Learning
May 15, 2024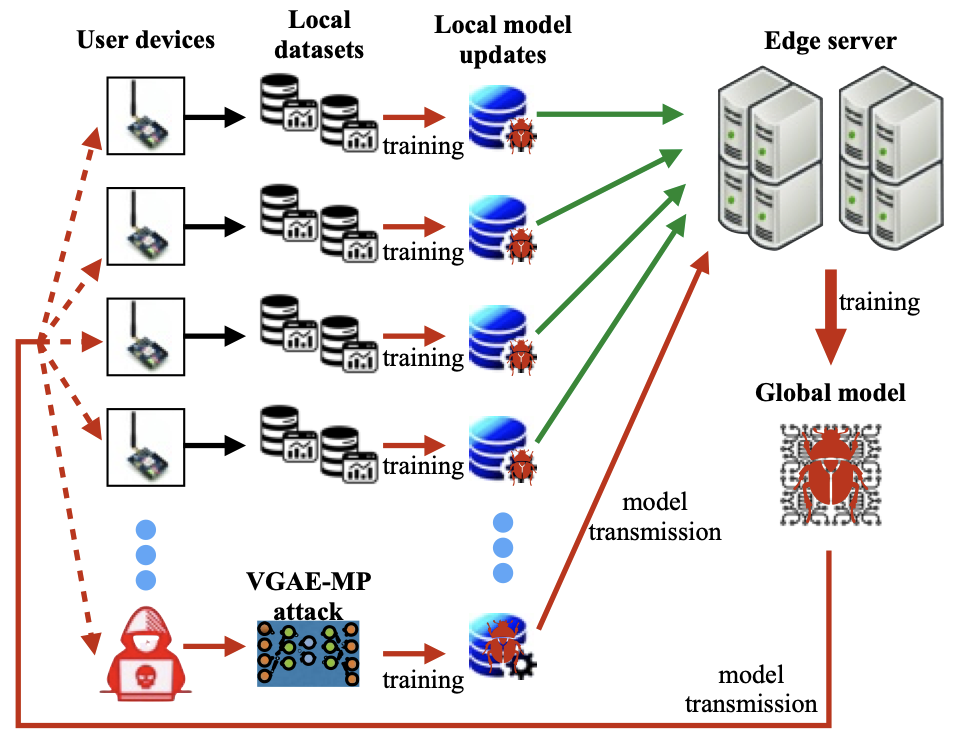
This paper puts forth a new training data-untethered model poisoning (MP) attack on federated learning (FL). The new MP attack extends an adversarial variational graph autoencoder (VGAE) to create malicious local models based solely on the benign local models overheard without any access to the training data of FL. Such an advancement leads to the VGAE-MP attack that is not only efficacious but also remains elusive to detection. VGAE-MP attack extracts graph structural correlations among the benign local models and the training data features, adversarially regenerates the graph structure, and generates malicious local models using the adversarial graph structure and benign models' features. Moreover, a new attacking algorithm is presented to train the malicious local models using VGAE and sub-gradient descent, while enabling an optimal selection of the benign local models for training the VGAE. Experiments demonstrate a gradual drop in FL accuracy under the proposed VGAE-MP attack and the ineffectiveness of existing defense mechanisms in detecting the attack, posing a severe threat to FL. Kai Li, Xin Yuan, Jingjing Zheng, Wei Ni, Falko Dressler and Abbas Jamalipour, "Leverage Variational Graph Representation For Model Poisoning on Federated Learning," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, May 2024. (online first)
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Kai Li, Xin Yuan, Jingjing Zheng, Wei Ni, Falko Dressler and Abbas Jamalipour, "Leverage Variational Graph Representation For Model Poisoning on Federated Learning," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, May 2024. (online first)
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Low-Complex Synchronization Method for Intra-Body Links in the Terahertz Band
April 16, 2024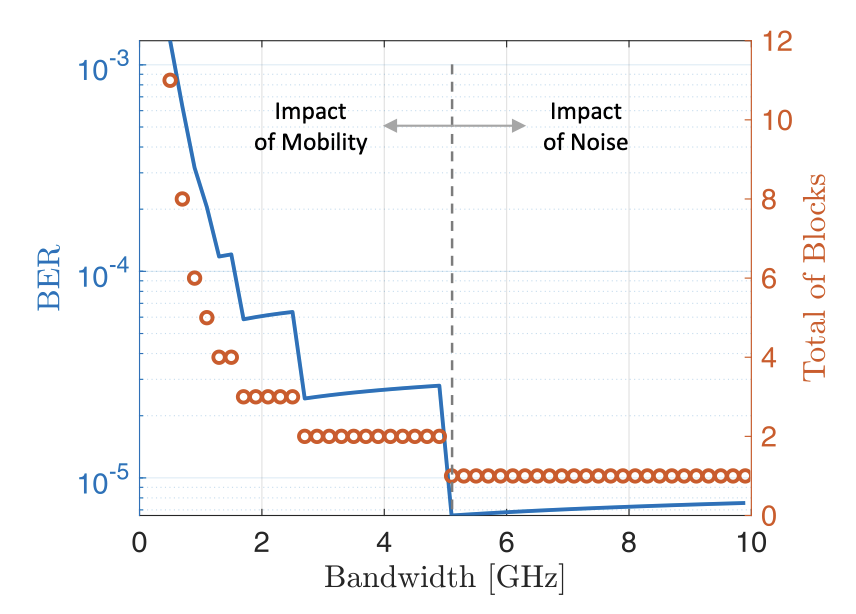
The recent literature focuses on deriving analytic channel models for intra-body links through the human tissues, including the analysis of achievable communication capacities in the terahertz band. A yet missing component, however, is a synchronization module to implement communication schemes in the intra-body link. Such synchronization module will ultimately bound the communication performance regarding the perceived signal to noise ratio (SNR) and bit error rate (BER), for instance. This paper contributes to the state of the art in two directions: (a) evaluating the bounds on the communication performance with the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for the synchronization symbol timing offset (STO) and (b) designing a low-complex mechanism to synchronize communication. Jorge Torres Gómez, Jennifer Simonjan and Falko Dressler, "Low-Complex Synchronization Method for Intra-Body Links in the Terahertz Band," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 42 (8), pp. 1967–1977, August 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Jorge Torres Gómez, Jennifer Simonjan and Falko Dressler, "Low-Complex Synchronization Method for Intra-Body Links in the Terahertz Band," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 42 (8), pp. 1967–1977, August 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Electric Circuit Representation of the Human Circulatory System to Estimate the Position of Nanosensors in Vessels
March 26, 2024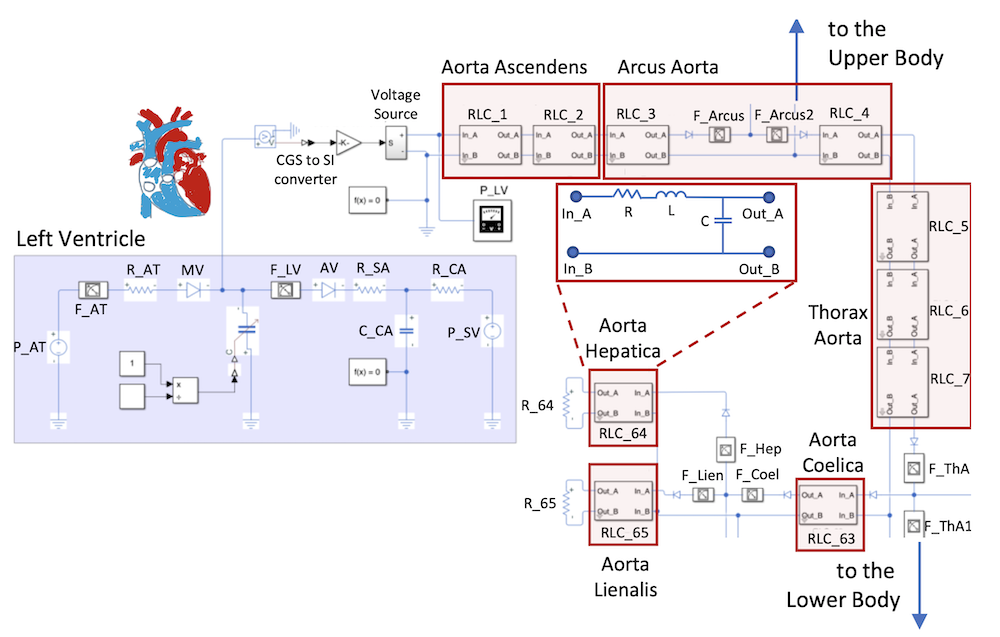
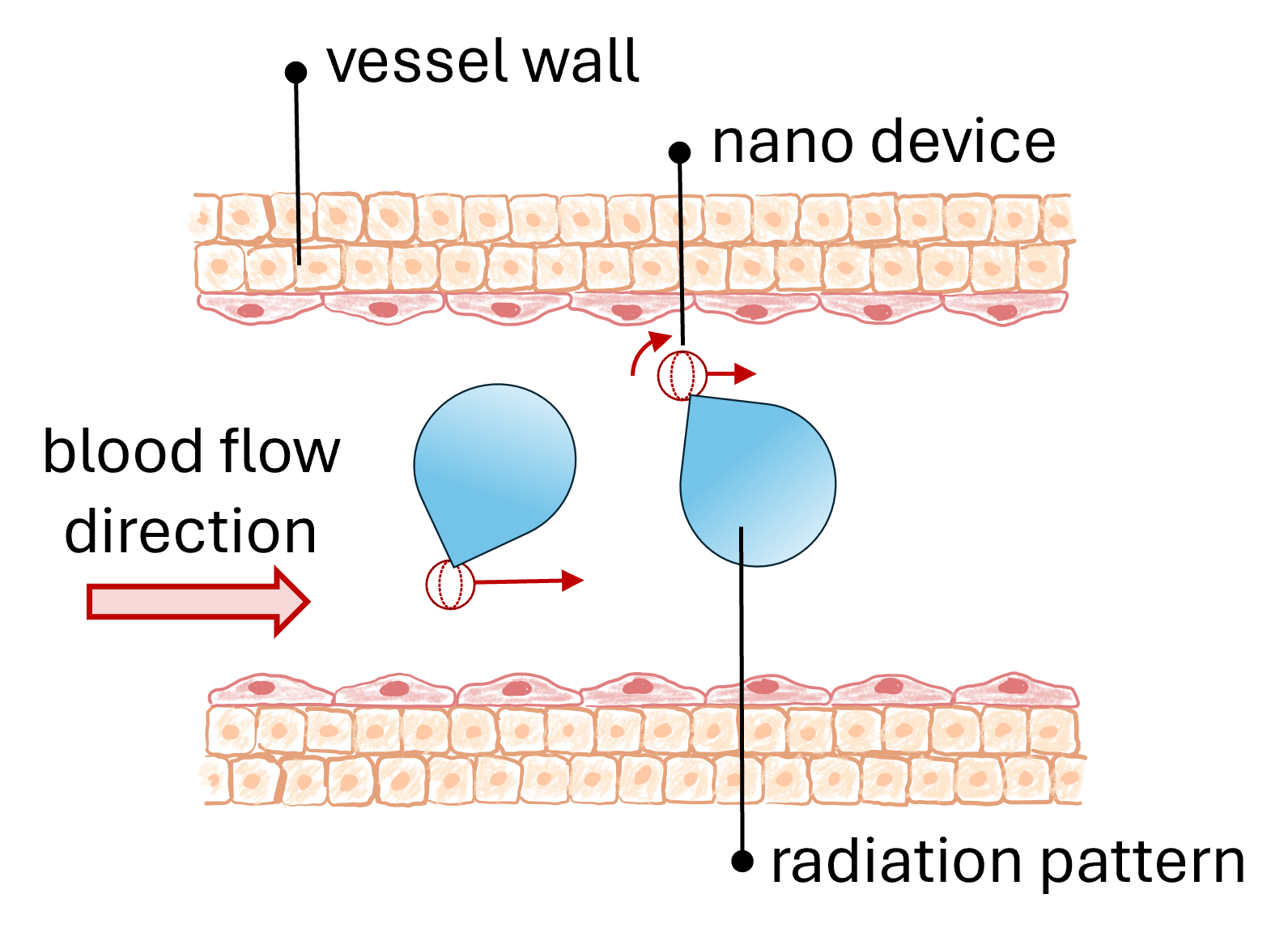
Nanodevices are the focus of research enhancing the detection and treatment of diseases in the human body. Focusing on the scenario where nanosensors are flowing with the blood in the human circulatory system (HCS), in this work, we investigate a model to predict their distribution along the various vessel segments. Although various approaches report solutions for localizing nanosensors in the body, it is also relevant to derive their stationary distribution along the vessel segments as a prior step to assess their actuation and sensing capabilities in the body. We use a Markov chain formulation to derive the stationary distribution of nanosensors. We evaluate the transition probabilities relying on the representation of vessels with electric circuit components. We implement the electric circuit representation of the left ventricle in the heart and the arteries to find the blood flow at vessel bifurcations and then compute the Markov chain probabilities. Our system also allows to reveal the dynamics of the movement of nanosensors during human activity. We illustrate results in two regimes as low and high activity to mimic the case when being at rest or doing sports. Jorge Torres Gómez, Jorge Luis González Rios and Falko Dressler, "Electric Circuit Representation of the Human Circulatory System to Estimate the Position of Nanosensors in Vessels," Elsevier Nano Communication Networks, vol. 40, pp. 100499, July 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Jorge Torres Gómez, Jorge Luis González Rios and Falko Dressler, "Electric Circuit Representation of the Human Circulatory System to Estimate the Position of Nanosensors in Vessels," Elsevier Nano Communication Networks, vol. 40, pp. 100499, July 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Side Effects of IRS: On the Need for Coordination in 6G Multi-Operator IRS-assisted Networks
February 15, 2024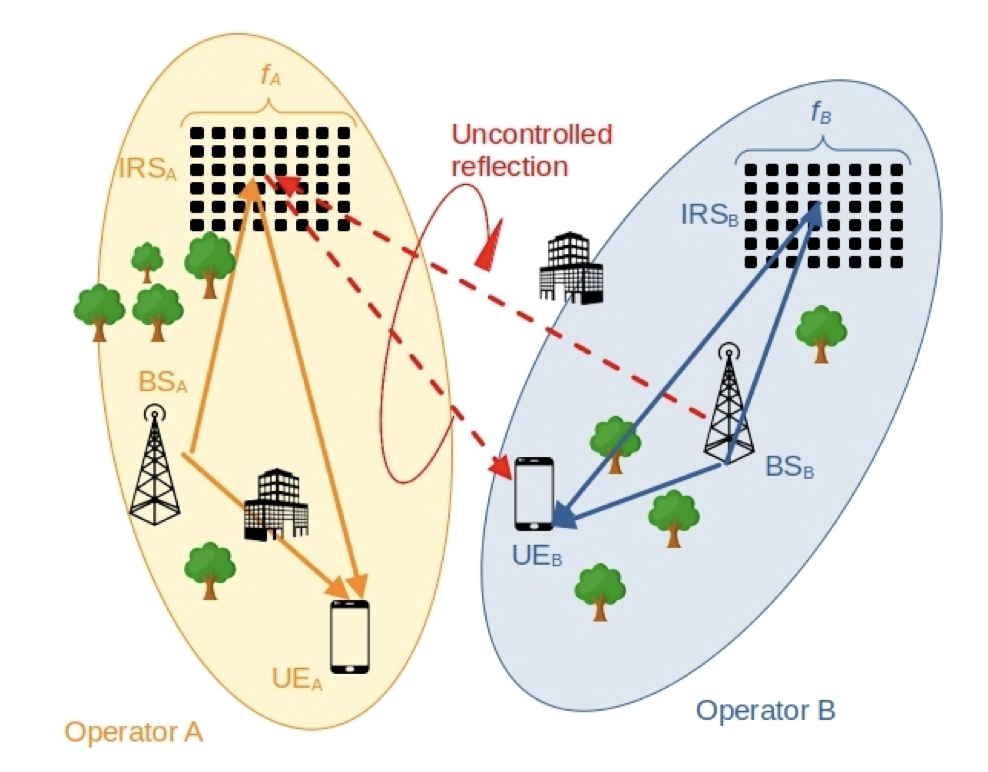
An IRS manipulates the channel propagation characteristics not only of signals of the operator who controls the IRS, but also of signals of other operators, although they operate at different frequencies. This is because IRS usually do not employ band pass filtering and, thus, also reflect signals of other frequencies. In this paper, we first introduce and discuss the problem of multi-operator coexistence issues that arise in IRS-assisted networks. We then propose splitting a single common IRS into multiple sub-blocks (subIRS) and controlling their dynamic assignment to operators, by taking into account the impact on the proximate operators as well. We show that the performance of the overall multi-operator network can be improved significantly if subIRS are properly assigned to the operators, compared to a purely static or random assignments. Our simulations results reveal that a significant improvement in terms of the sum rate and the fairness with respect to the respective data rate of the operators can be achieved. Joana Angjo, Anatolij Zubow and Falko Dressler, "Side Effects of IRS: On the Need for Coordination in 6G Multi-Operator IRS-assisted Networks," Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2023), 4th Workshop on Emerging Topics in 6G Communications (6GComm), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, December 2023, pp. 1380–1385.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Joana Angjo, Anatolij Zubow and Falko Dressler, "Side Effects of IRS: On the Need for Coordination in 6G Multi-Operator IRS-assisted Networks," Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2023), 4th Workshop on Emerging Topics in 6G Communications (6GComm), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, December 2023, pp. 1380–1385.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Distributed UWB-based Ranging for Particle Tracking in Avalanches
January 30, 2024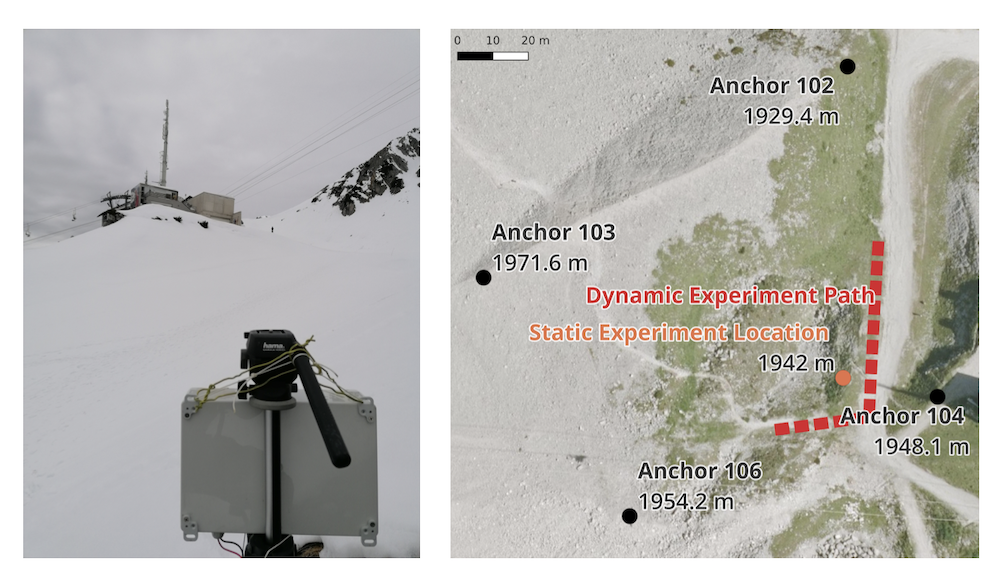
The inner dynamics and transport mechanisms of avalanches - especially on a particle level - remain hidden for most observation approaches. In this paper, we present a particle based, distributed tracking system that is based on ultra-wideband (UWB) ranging and localization. UWB-based positioning is particularly challenging in outdoor scenarios covering large distances in complex topography and fast moving, mobile systems. Our system model considers multiple anchor nodes distributed with inter-node distances in the order of a few hundred meters. Mobile nodes, which move with the avalanche in the field, are tracked via UWB measurements. We present our prototype and demonstrate through first experiments the general feasibility of UWB-based tracking in snow environments. Jonas Kuß, Anselm Köhler, Michael Neuhauser, Rene Neurauter, Johannes Gerstmayr, Jan-Thomas Fischer and Falko Dressler, "Distributed UWB-based Ranging for Particle Tracking in Avalanches," Proceedings of 19th IEEE/IFIP Conference on Wireless On demand Network Systems and Services (WONS 2024), Chamonix, France, January 2024, pp. 125–132.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Jonas Kuß, Anselm Köhler, Michael Neuhauser, Rene Neurauter, Johannes Gerstmayr, Jan-Thomas Fischer and Falko Dressler, "Distributed UWB-based Ranging for Particle Tracking in Avalanches," Proceedings of 19th IEEE/IFIP Conference on Wireless On demand Network Systems and Services (WONS 2024), Chamonix, France, January 2024, pp. 125–132.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Empowering the 6G Cellular Architecture with Open RAN
December 01, 2023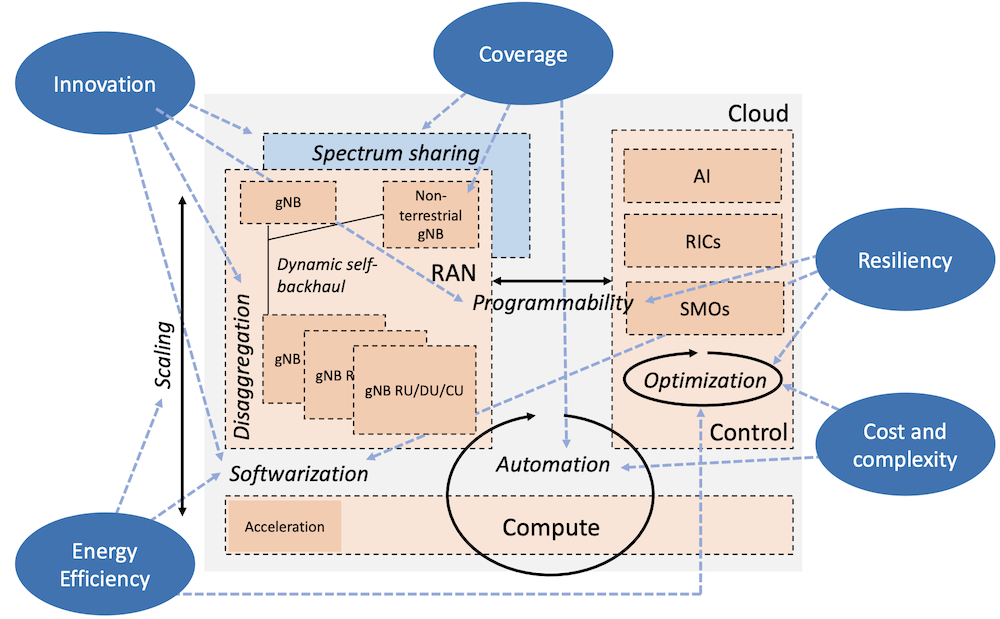
In this paper, we highlight the transformative potential of embracing novel cellular architectures by transitioning from conventional systems to the progressive principles of Open RAN. This promises to make 6G networks more agile, cost-effective, energy-efficient, and resilient. It opens up a plethora of novel use cases, ranging from ubiquitous support for autonomous devices to cost-effective expansions in regions previously underserved. The principles of Open RAN encompass: (i) a disaggregated architecture with modular and standardized interfaces; (ii) cloudification, programmability and orchestration; and (iii) AI-enabled data-centric closed-loop control and automation. We first discuss the transformative role Open RAN principles have played in the 5G era. Then, we adopt a system-level approach and describe how these Open RAN principles will support 6G RAN and architecture innovation. We qualitatively discuss potential performance gains that Open RAN principles yield for specific 6G use cases. For each principle, we outline the steps that research, development and standardization communities ought to take to make Open RAN principles central to next-generation cellular network designs. Michele Polese, Mischa Dohler, Falko Dressler, Melike Erol-Kantarci, Rittwik Jana, Raymond Knopp and Tommaso Melodia, "Empowering the 6G Cellular Architecture with Open RAN," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 42 (2), pp. 245–262, February 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Michele Polese, Mischa Dohler, Falko Dressler, Melike Erol-Kantarci, Rittwik Jana, Raymond Knopp and Tommaso Melodia, "Empowering the 6G Cellular Architecture with Open RAN," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 42 (2), pp. 245–262, February 2024.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Explainability of Neural Networks for Symbol Detection in Molecular Communication Channels
November 05, 2023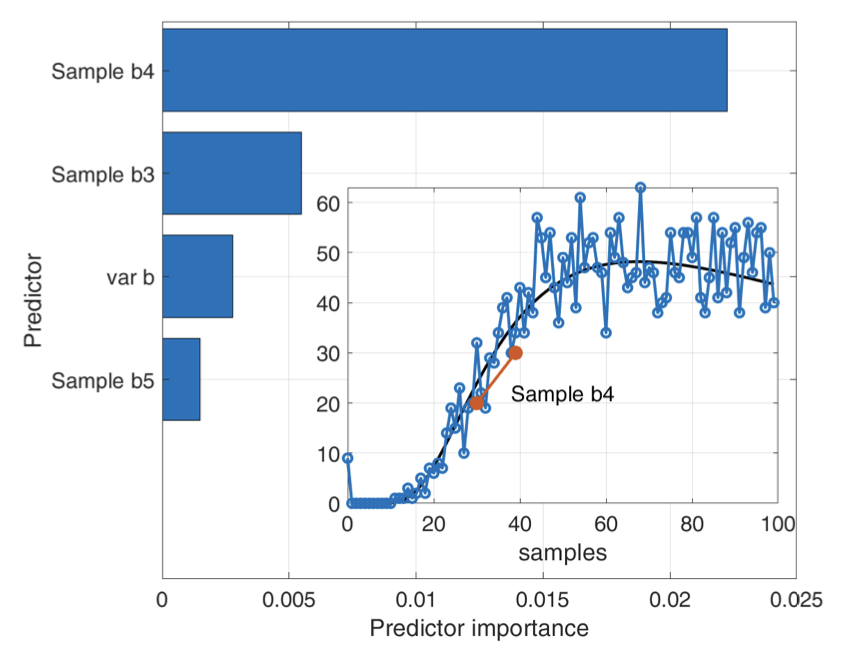
Recent research in molecular communication (MC) suggests machine learning (ML) models for symbol detection, avoiding the unfeasibility of end-to-end channel models. However, ML models are applied as black boxes, lacking proof of correctness of the underlying neural networks (NNs) to detect incoming symbols. This paper studies approaches to the explainability of NNs for symbol detection in MC channels. Based on MC channel models and real testbed measurements, we generate synthesized data and train a neural network (NN) model for the detection of binary transmissions in MC channels. Using the local interpretable model-agnostic explanation (LIME) method and the individual conditional expectation (ICE), the findings in this paper demonstrate the analogy between the trained NN and the standard peak and slope detectors. Jorge Torres Gómez, Pit Hofmann, Frank H. P. Fitzek and Falko Dressler, "Explainability of Neural Networks for Symbol Detection in Molecular Communication Channels," IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 9 (3), pp. 323–328, September 2023.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Jorge Torres Gómez, Pit Hofmann, Frank H. P. Fitzek and Falko Dressler, "Explainability of Neural Networks for Symbol Detection in Molecular Communication Channels," IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 9 (3), pp. 323–328, September 2023.
[DOI, BibTeX, PDF, More details]
Load all older featured papers
Last modified: 2023-10-07